What distinguishes MVC, MVP, MVVM, MVVM-C, and VIPER architecture patterns from each other?
Introduction
When it comes to software development, choosing the right architecture pattern can make a huge difference in the quality and maintainability of the codebase. There are several architecture patterns to choose from, including MVC, MVP, MVVM, MVVM-C, and VIPER. While all of these patterns share some similarities, they each have their own unique characteristics and are best suited for different types of applications. These architectural patterns are among the most commonly used in development.
Developers have introduced them to overcome the limitations of earlier patterns. So how do they differ?🤔
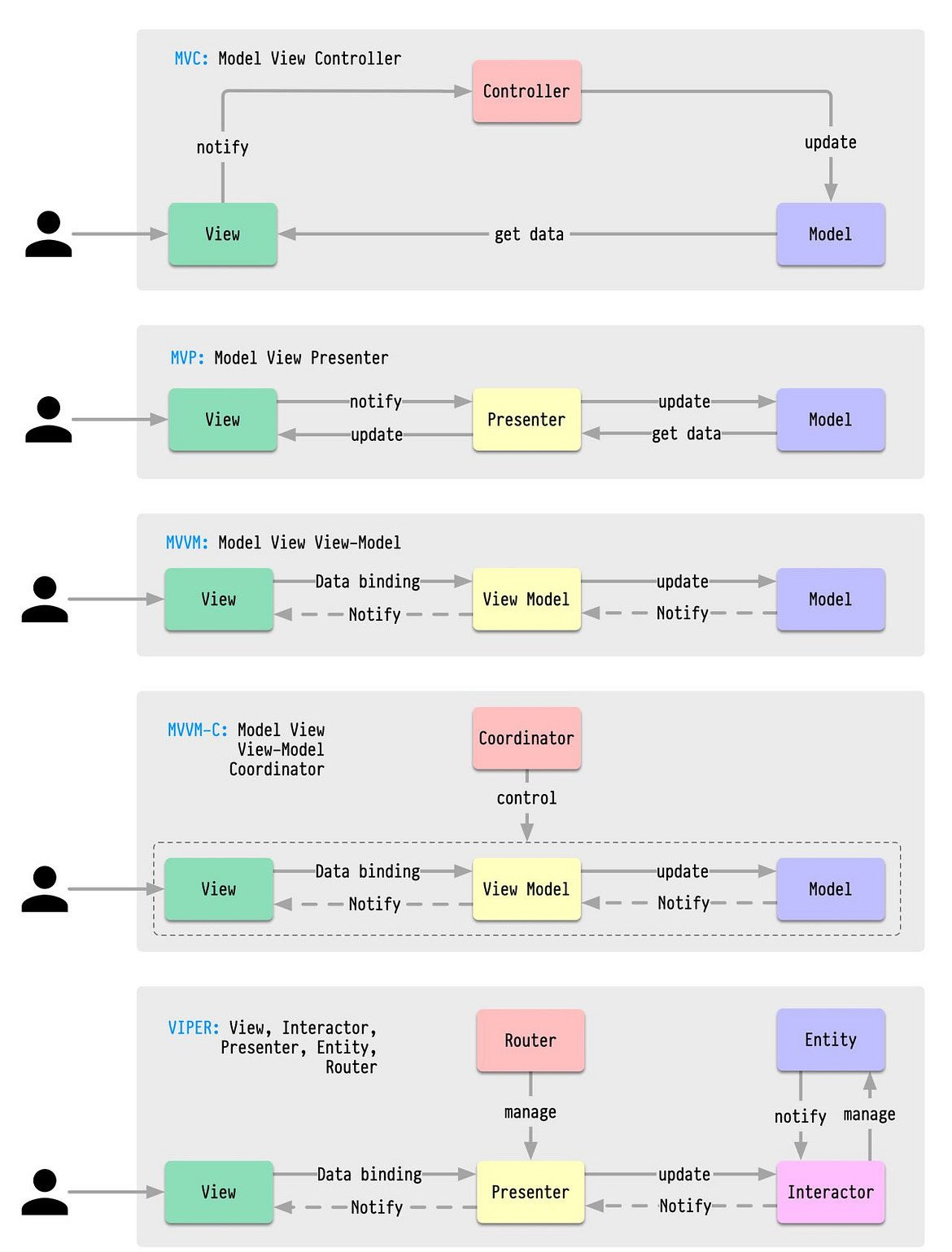
⚡MVC (Model-View-Controller)
MVC is one of the most well-known and widely used architectural patterns. It separates the application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller. The model represents the data and the business logic, the view is responsible for rendering the user interface, and the controller acts as the intermediary between the model and the view.
⚡MVP (Model-View-Presenter)
MVP is similar to MVC, but with a slightly different approach. In MVP, the presenter acts as an intermediary between the model and the view, rather than the controller. The presenter is responsible for updating the view with data from the model, and for handling user input and events.
⚡MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel)
MVVM is another architectural pattern that is gaining popularity. It is similar to MVP, but with the addition of a view model. The view model is responsible for managing the state of the view, as well as providing data from the model to the view. This pattern is often used in applications that require complex user interfaces.
⚡MVVM-C (Model-View-ViewModel-Coordinator)
MVVM-C is a variation of MVVM that adds a coordinator to the mix. The coordinator is responsible for handling navigation between different screens or views within the application. This pattern is useful for applications that have multiple screens or views that need to be managed.
⚡VIPER (View-Interactor-Presenter-Entity-Router)
VIPER is a relatively new architectural pattern that has gained popularity in recent years. It is similar to MVC, but with the addition of several new components, including the interactor, entity, and router. The interactor is responsible for handling business logic, the entity represents the data, and the router handles navigation between different screens or views.
🫡Common points to remember:
MVC, the oldest pattern, dates back almost 50 years
Every pattern has a “view” (V) responsible for displaying the user content interface and receiving the user input
Most patterns include a “model” (M) to manage the business data and logic
“Controller”, “Presenter”, and the “View-Model” are translators that mediate between the views and the model. Other than this, the VIPER pattern contains the “entity” and “router” translator which represents the data and network routing.
These translators can be quite complex to write, so various patterns have been proposed to make them more maintainable.
🤔Self Activity:
Over to you: keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list of architectural patterns. Other notable patterns include Flux and Redux. How do they compare to the ones mentioned here?👀
Conclusion
In conclusion, while all of these architectural patterns share some similarities, they each have their own unique characteristics and are best suited for different types of applications. Choosing the right architecture pattern can make a huge difference in the quality and maintainability of the codebase, so it's important to take the time to understand the pros and cons of each pattern before making a decision.
That's all for today.
Share your feedback, and if you like it, then kindly retweet the first tweet😀
New to my profile?🎉
Hey! I am Ayush, a full-stack developer from India. I tweet and document my coding journey🌸
Follow @ayushsoni1010 for more such content🔥😉